MSFS2024 COMPATIBILITY
- Flight model is partially broken, too fast reaction on user controls
- Avionics partially working
Wait for further update before use!
The Kamov Ka-10 (NATO reporting name Hat) is a Soviet single-seat observation helicopter that first flew in 1949.
Design and development
The Ka 10 was a development of Nikolay Kamov’s earlier Ka-8, which had been successful enough to allow Kamov to set up his own OKB (design bureau) in 1948. The Ka-10 made of similar layout to the Ka-8, with an open steel-tube structure carrying an engine, a pilot’s seat and two three-bladed coaxial rotors. It was larger, however, with a revised transmission and rotor hub design, and a new engine specially designed for the helicopter, the 41 kilowatts (55 hp) Ivchenko AI-4 flat-four.
Operational history
The Ka-10 made its first flight in September 1949. Three more prototypes followed, which were evaluated by Soviet Naval Aviation. A Ka-10 was displayed at the 1950 Tushino Air Display, and one made the first landing by a Soviet helicopter on the deck of a ship on 7 December 1950.
In 1954, 12 of an improved version, the Ka-10M were built for the Maritime Border Troops. They had a twin tail rather than the single vertical fin of the Ka-10 and modified rotors and control systems.
MSFS Ka-10M features
- native helicopter flight model with CFD simulation
- accurate weight and size
- multiple liveries
- animated mechanics – control levers, rotor mast
- animated default pilot model (IK bones)
- kneel tablet with navigation map (Pelican’s nav MFD)
- custom downwash effects
- custom engine, gear and rotor WWISE sounds
- Kuznetsov carrier group is a part of Ka-10M package
Availability
Ka-10M “HAT” helicopter & Kuznetsov carrier group package price tag is about $6
MSFS marketplace – PC and XBOX v1.x (Ka-10M with custom flight model, v2 update should be released in late December)
SimMarket – PC only v2.x (Ka-10M with native flight model + Kuznetsov carrier group)
Planned improvements
- Landable Kuznecov aircraft carrier (Nov 2022)
- Native flight model (Nov 2022)
- Failures and voice assistance (English, Russian and Chinese languages) (Jan 2022)
- Landable and controllable cargo truck (SimUpdate12)
Credits
- Project management and aircraft configuration – thealx (TouchingCloud)
- Modelling – Mykrode (GOT Friends)
- Texturing – 270inc (GOT Friends)
- MIsc modelling and texturing – Cyrus Smith (TouchingCloud)
- Flight model fixes and carrier scenery creation – SpacerPlay
- Map layout – CaptnJackBilbo
Ka-10M Specifications
General characteristics
- Crew: one
- Length: 3.70 m (12 ft 1.75 in) (fuselage length)
- Height: 2.5 m (8 ft 2.5 in)
- Empty weight: 249 kg (548 lb)
- Gross weight: 390 kg (860 lb)
- Powerplant: 1 × AI-4G , 40 kW (55 hp)
- Fuel amount: 33 liters (8.7 gal)
- Main rotor diameter: 2 × 6.12 m (20 ft 1 in)
- Main rotor area: 2 × 58.8 m2 (633 sq ft)
Performance
- Maximum speed: 120 km/h (74 mph, 65 kn)
- Range: 150 km (93 mi, 81 nm)
- Service ceiling: 2,500 m (8,200 ft)
Paintkit
Paintkit is a collection of the livery creators, contains: textures (*.png), livery package example, UV layouts (*.png), textures sources (*.xcf)
Download paintkit from Google Drive
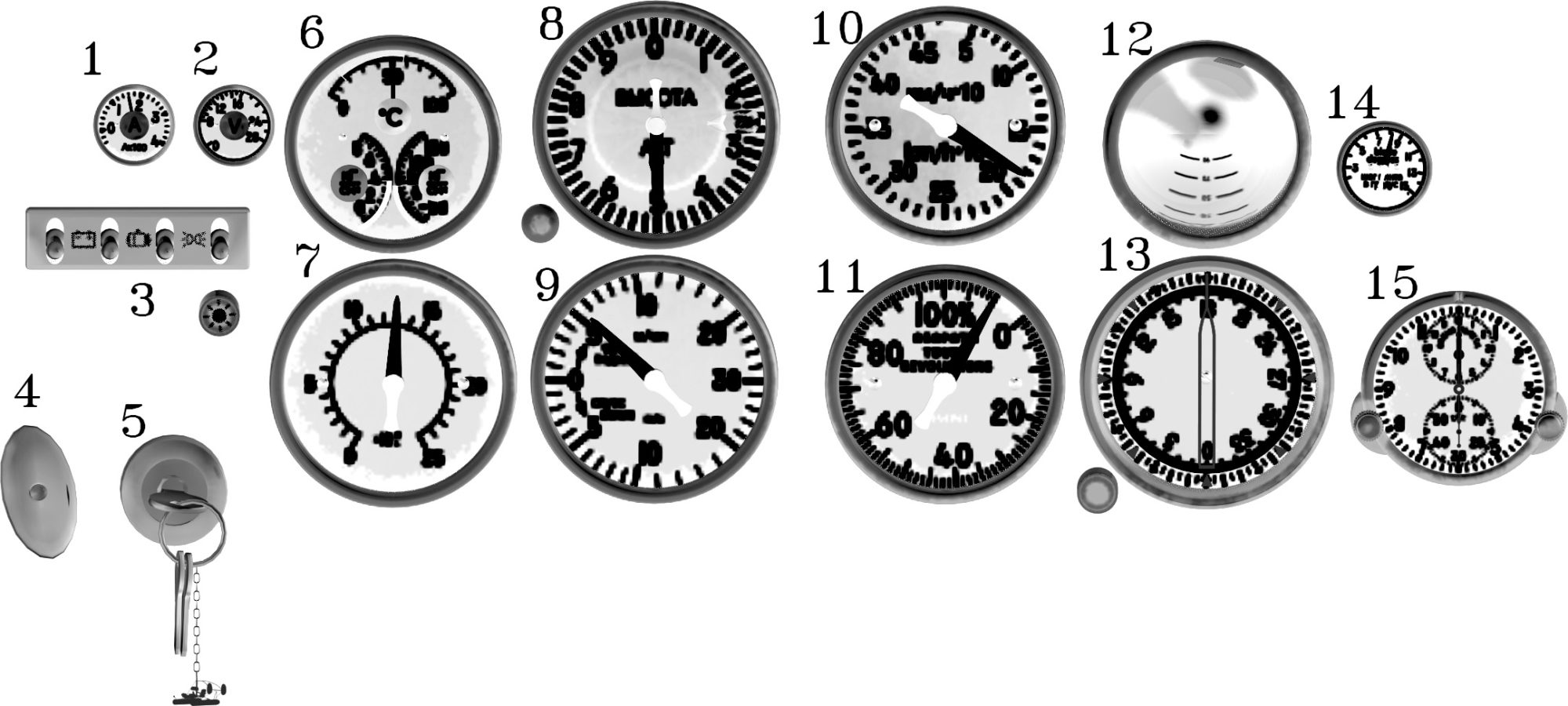
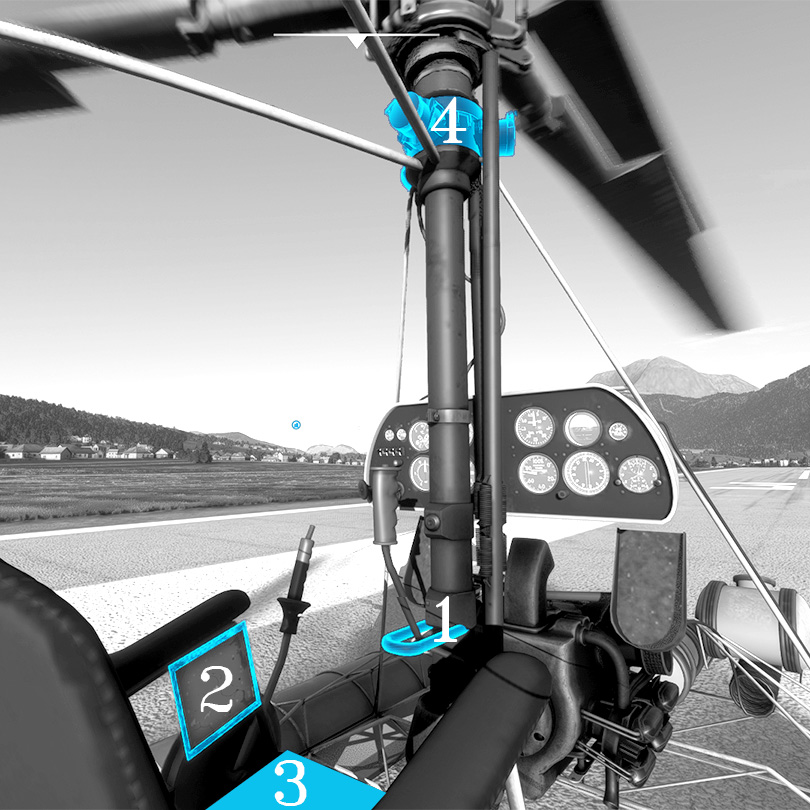
1. Instruments
1.1. Front panel
1.1.1. Battery voltage indicator – discharged if value less than 24V, charged – 24V or higher
1.1.2. Battery power consumption – discharges if value higher than 0 amps, charges if lower.
1.1.3. Electrical switches:
- main battery switch – required for helicopter electronics to operate before engines start
- alternator switch – recharges battery and supplies electronics with power during flight
- landing light switch – toggles front lamp power
- navigation lights switch – toggles rear lamps power
- gauges light knob – changes instruments backlight brightness
1.1.4. Mixture handle – controls fuel/oxygen proportion, no fuel flow in close position.
1.1.5. Magneto key – enables magnetos, activates starter in far right position (no automatic start available, hold key until engine combustion appears). Keychain can be read as a motion vectors indicator – it is affected by body acceleration and gravity vectors.
1.1.6. Engine parameters:
- oil temperature, units – Celsius
- fuel pressure, units – kg/cm2
- oil pressure, units – kg/cm2
1.1.7. Fuel quantity indicator, units – litres
1.1.8. Altitude indicator, units – meters. Knob adjusts base air pressure, units – mmHg.
1.1.9. Vertical speed indicator, units – m/s
1.1.10. Airspeed indicator, units – km/h
1.1.11. Engine RPM indicator, units – percent of max RPM
1.1.12. Attitude indicator. Inop flag disappears after gauge powered up.
1.1.13. Magnetic poles indicator, units – degrees. Knob adjusts magnetic deviation.
1.1.14. Rotor blades pitch angle indicator, units – degrees
1.1.15. Clock with a timer. Left knob start and reset timer, right knob adjusts time value
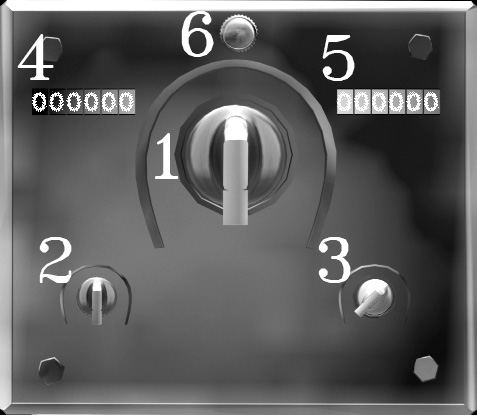
1.2. Radio
1.2.1. Standby frequency MHz knob
1.2.2. Standby frequency KHz knob
1.2.3. Volume knob (left position – off)
1.2.4. Active frequency
1.2.5. Standby frequency
1.2.6. Swap active and standby frequencies
1.3. Misc controls
1.3.1. Toggle yoke visibility (cockpit only)
1.3.2. Toggle knee tablet with map position
1.3.3. Toggle pilot visibility (cockpit only)
1.3.4. Toggle rotor blades visibility (cockpit only)
2. Operation manual
2.1. Cold start
2.1.1. Ensure you are on a flat surface and there are no obstacles (buildings, trees, aircraft or vehicles) in a 50m radius from you
2.1.2. Turn on main battery switch (1.1.3)
2.1.3. Turn on gauge backlight if required (1.1.3)
2.1.4. Ensure battery power at least 24 volts (1.1.1)
2.1.5. Ensure you have enough fuel for your flight (1.1.7). Calculation formula – 13 litres per each 100km of flight + 5 litres for take-off and landing procedures
2.1.6. Pull the fuel mixture handle to its maximum position (1.1.4).
2.1.7. When ready, turn the magneto key to the far right position (1.1.5). Combustion should be started shortly, release the key. If not – release the magneto key, ensure you have enough fuel and fuel mixture set in the proper position. Try again. If still fails – start engine automatically with Ctrl + E keys.
2.1.8. After engine start, turn on alternator switch (1.1.3)
2.1.9. Wait until oil temperature reaches 30°C(1.1.6)
2.1.10. Raise collective handle on one half, you should hear how engine RPM increases, oil temperature and pressure will raise.
2.1.11. Turn on clutch with red switch on the collective – rotor will start to spin up.
2.1.12. Wait until rotor RPM reaches 80%
2.2. Take-off
2.2.1. Slowly push mixture handle until RPM needle will go down, then pull handle back on about 5% (1.1.4). This way you will get optimal fuel consumption for current conditions.
2.2.2. Enable navigation lights (1.1.3)
2.2.3. Enable landing light if required (1.1.3)
2.2.4. Raise collective slowly until helicopter lift off
2.2.5. Hover for 1 minute ~1 meter above ground, engine RPM should be stable (around 100%), no lift losses should be experienced.
2.2.6. Raise collective to maximum and pitch down a bit to gain forward velocity. Follow the flight plan route.
2.3. Landing on solid surface
2.3.1. Head to the landing area
2.3.2. Hold such airspeed and vertical velocity so you will approach the landing area at 10 meters altitude above ground level.
2.3.3. Right before you reach the landing area, pitch up and transit into hovering.
2.3.4. Hold sink velocity near 0.5-1 m/s, do not exceed this value to avoid vortex ring appearance.
2.3.5. After landing, lower collective to minimum
2.4. Landing on water
2.4.1. Head to the chosen water reservoir
2.4.2. Hold 50km/h airspeed and 1m/s sink rate until you touch the water surface
2.4.3. Right before touchdown, pitch up to avoid the flip
2.4.4. After touchdown, set the collective lever to half position and float to the chosen dock
2.5. Shutdown
2.5.1. Lower collective to bottom position
2.5.2. Disable clutch
2.5.3. Set mixture handle to zero to cut engine fuel supply (1.1.4)
2.5.4. Set magneto key to far left position (1.1.5)
2.5.5. Turn off lights, alternator, battery switches
2.6. Emergency landing
In case of engine failure or fuel low during flight, the rotor will no longer create lift and you will need to perform autorotation landing.
During autorotation aircraft glide with constant vertical (negative) and forward (positive) speed at such pitch angle so airflow spin up the rotor and create air resistance. Important to understand that final rotor RPM depends on total velocity (higher velocity – higher rotor RPM) and rotor blade pitch (higher pitch angle – lower rotor RPM). You have to avoid rotor RPM to exceed 100% as it will cause gear damage, use the collective to keep RPM around 80%-100%.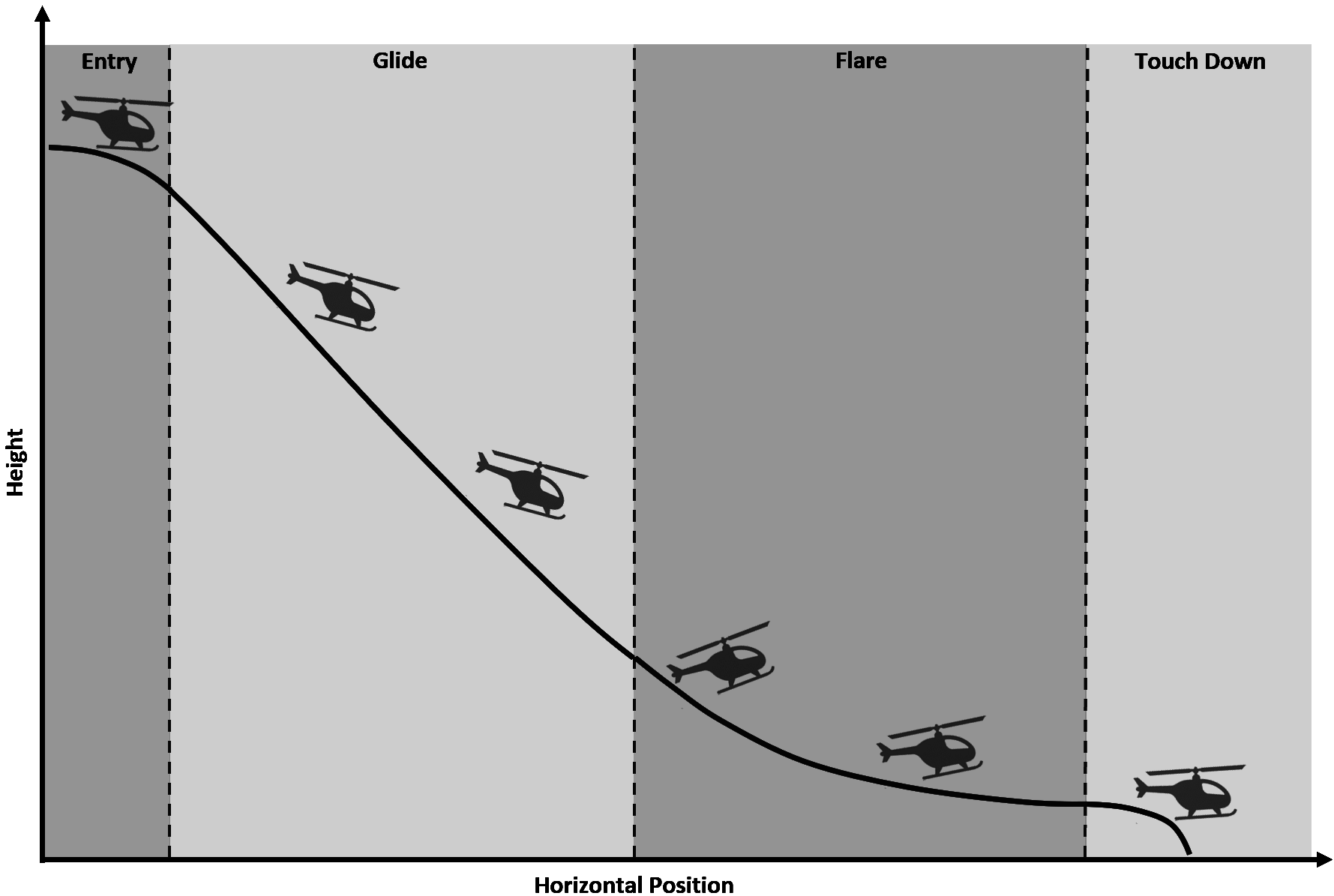
2.6.2 When your rotor RPM reach at least 80% transit into glide – pitch up so rotor RPM stays constant while sink rate is about 5m/s
2.6.4 ~5 seconds before touchdown transit into flare – pitch up and raise collective about 1/2 or 2/3 to decrease sink rate to 1m/s
2.6.5 Right before touchdown level helicopter to land smoothly
3. Controls
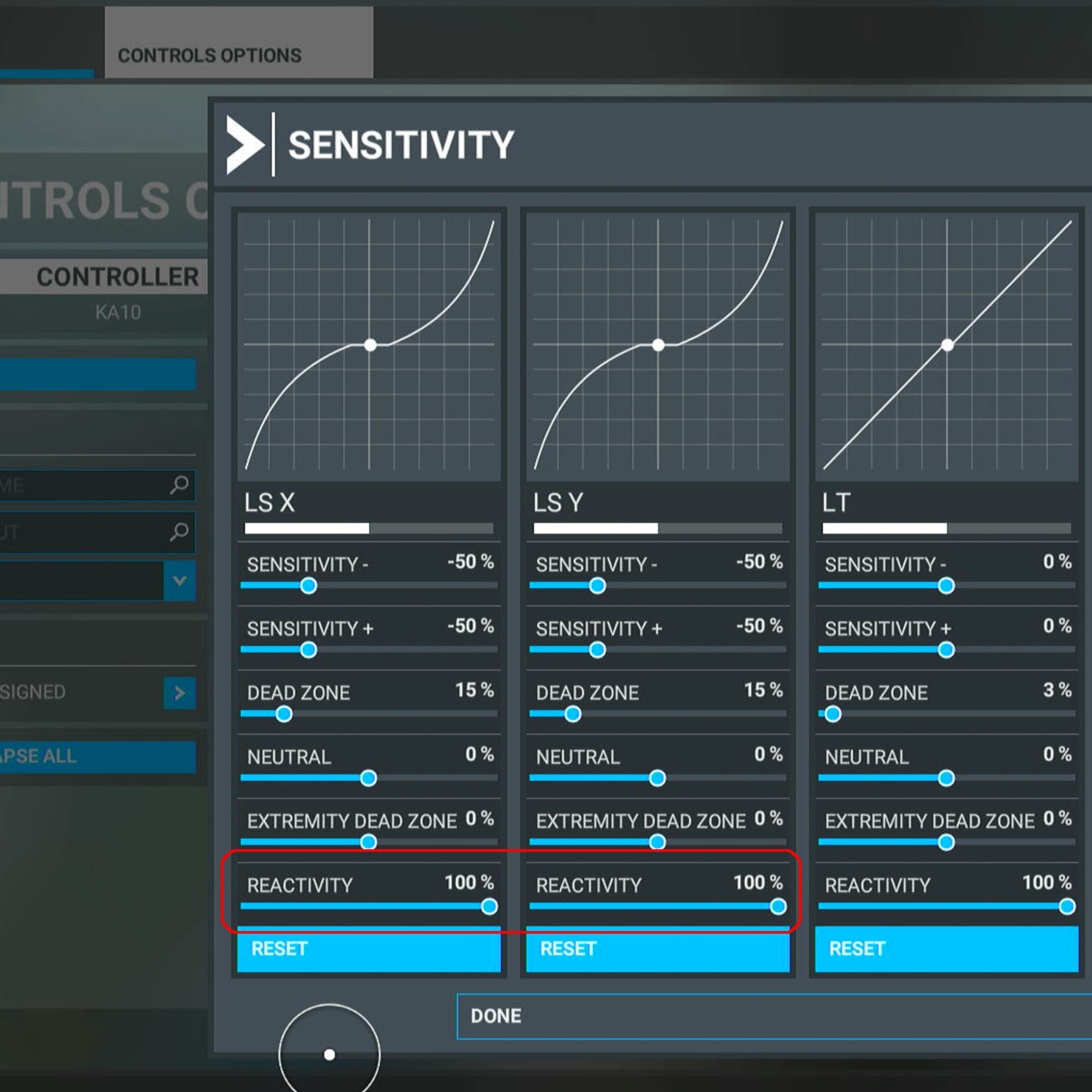
3.1 CONTROL STICK SENSITIVITY
For gamepad users (most XBOX owners) Increase REACTIVITY value of left stick (both axes to max). You can create new preset “KA10” to switch between them easily anytime.
Reason – reactivity makes aileron and elevator react smoothly on your actions, but chopper require quick controls as it does not have any kind of stabilization helpers.
3.2 CONTROL STICK TRIM
Even if original helicopter does not have trimming, you still can use it in MSFS.
For XBOX gamepad: after you transit from hovering into cruise flight, hold RB and RIGHT STICK FORWARD. At some point you will be able to release LEFT STICK into neutral position and continue the flight with forward velocity
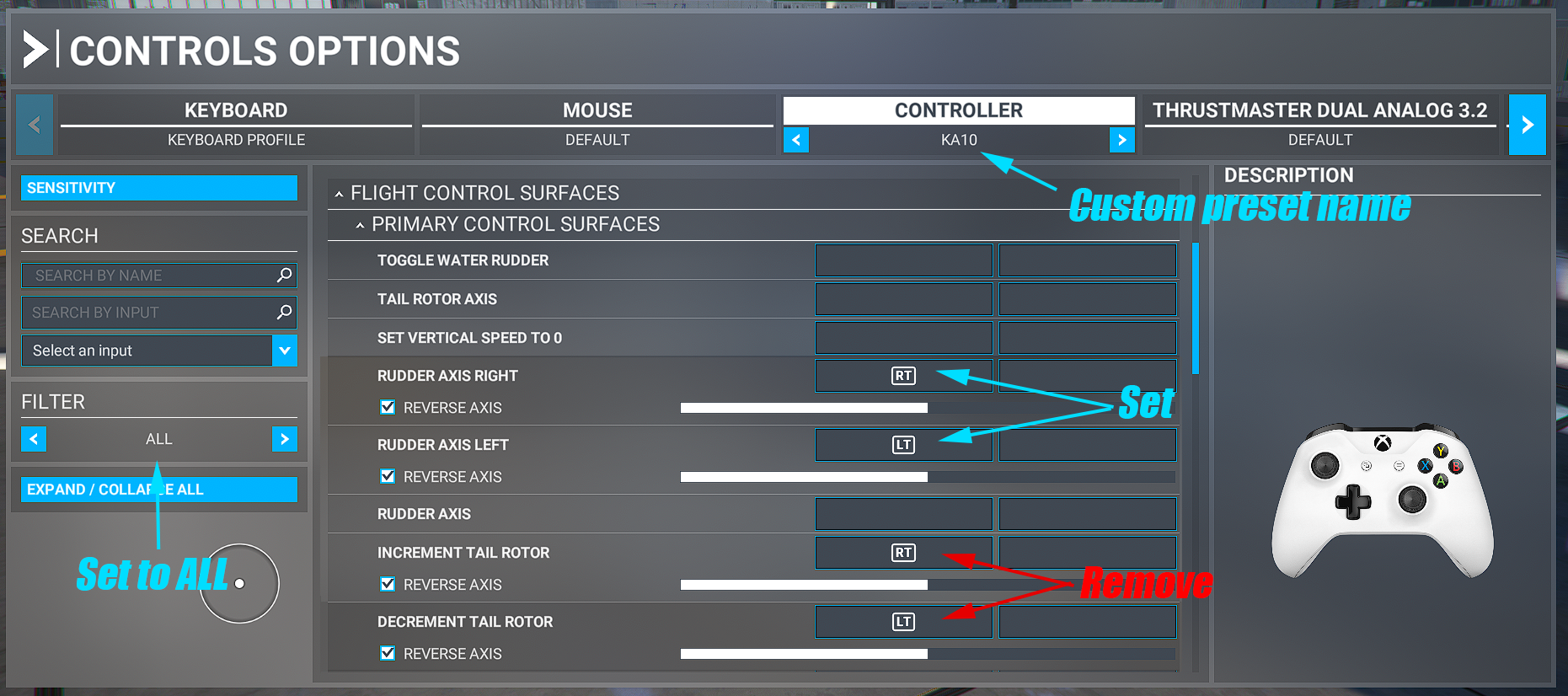
3.3 TAIL ROTOR CONTROLS
In the default Helicopter controls preset left and right triggers of Xbox controller used as Tail Rotor trim. However, Ka-10M does not have tail rotor so there is no torque moment created by its rotation. To make turn controls more comfortable, you can assign LT and RT triggers to the Rudder Axis events, and remove them from the Increment/Decrement Tail Rotor. This way it will work similar to the airplane rudder controls – reset to neutral once trigger released.
4. Failures
4.1. Rich fuel mixture
During flight, you may experience engine power loss, in rare case – combustion failure. To prevent it:
- ensure you have set optimal mixture handle position
- avoid to lower collective handle too fast – otherwise fuel pressure will be not able to normalize quickly enough and sparks will get wet in result
4.2. Rotor blades frost
During flight through the clouds or mist at low temperature conditions, blades may be affected by icing. This helicopter does not have blades heater or any kind of icing detection, so you need to control icing level visually.
If icing condition is heavy which affect flight dynamics, perform landing immediately.
Ka-10M “HAT” v2.8.0
3 liveries added: Egypt, Hungary, Switzerland
DEMO version!
Please consider about purchasing this product in Microsoft Flight Simulator marketplace
Download from cloud / Purchase payware versionKa-10M “HAT” v2.7.1
FIX: carrier crew appear for Piper Comanche 250 by A2A
Ka-10M “HAT” v2.7.0
Ka10M fixes:
Oil and fuel pressure gauges wrong value
Carriers issues fixed:
steam does not appear when carrier crew inserted manually
teleport to deck not available if time sync disabled
teleport to deck inaccuracy
native wires too weak to stop aircraft in time: enable Catapult and Arrestors feature but without Fake tailhook, compatible with any aircraft carrier wich has native wires installed
aircraft pitch up during catapult launch
New features:
OLS tab added
Animated rescue helicopter
Ka-10M “HAT” v2.6.0
- wrong Izmir carrier teleport coordinates fixed
- Ka-10M pilot camera position changed
- Ka-10M artificial horizon backlight flickering fixed
- aircraft carrier catapult crew support added to Carriers Panel
- guide and launcher crew members added on Kuznetsov (has no catapult IRL)
Ka-10M “HAT” v2.5.1
– TopGun carriers added to 7 locations (Maverick add-on has to be installed, optionally – PBK crew)
– 3 Additional Kuznetsov locations
– parked on Kuznetsov aircraft no longer float in the air after flight restart
– panel styles issues fixed for 4K screen resolution
– Kirov cruiser model updated
– Ka-10 yaw resistance increased
– Carrier Controls panel user interface issues fixed
– custom arresting and catapult scripts works even when Carrier Controls panel is closed
– custom arresting script may be used together with native arrestors to prevent overrun
– rotor stops spinning after engine shut down
– spotlights direction control for USS carriers
– Carrier Controls active tab restores after panel closed
– PBK crew model included (for F/A-18SW compatibility)
Ka-10M “HAT” v2.3.0
Issues fixed:
– wake effects does not appear if Maverick pack not installed
– OLS disappear at very short distance
– buttons of the panel near border are not clickable
Ka-10M “HAT” v2.2.1
Carrier:
– carrier settings will be stored until next flight (only if Ka-10M is selected aircraft)
– custom arresting simulation for airplanes without tailhook configured (no wires animation)
– ILS (109.5) and TACAN (x33) added for static carrier (Istanbul)
– helipad and runway start point added for static carrier (Istanbul)
– teleport to the carrier buttons added to panel (available only while real time sync is active)
– quick pushback simulation improved
– carrier group time sync respawn interval increased to 30 minutes
Ka-10M “HAT” v2.1.1
Carrier:
– new location: Istanbul (Middle East, anchored)
– arresting wires position precision improved
Ka-10M “HAT” v2.1.0
Carrier:
– deck collision improved, extra surface added under the runway to prevent wheels sinking
– added collision surfaces for safety barriers
– LODs added for carrier and static aircraft (loss of details at higher distance for performance sake)
– carrier group speed decreased to ~15 knots (average cruise speed in RL)
Helicopter
– rotor icing cause lift loss, sound change and partial loss of controls (custom script)
– collective handle set to 0% when appear on runway
– collective handle animation variable change from throttle to collective
– additional switch added to the panel for manual throttle control (fictional)
Ka-10M “HAT” v2.0.0
Carrier:
– deck collision issues fixed, surface area increased to cover safety barriers
Ka-10M:
– downwash effect improved
– clutch added (top of the collective handle, first engine start initiated, then clutch switch toggled)
– controls and rotor sounds linked with new variables (issue: rotor whining appear only while engine combustion happen)
– engine sound cone removed (sounds same from any direction)
– custom yaw force simulation
– weights and fuel consumption adjusted
– electrics restored from early version of Ka-10M



















32 feedbacks on Ka-10M “HAT”
Dear Touching Cloud staff!
My KA10-M, which is inherited from MSFS2020 exits during load the flight in MSFS2024.
Did you experienced / got feedback about this situation?
Thank in advance.
Miklos
Dear development team. I love the Kamov Ka10 coaxial helicopter. It works fine with MSFS2020. Unfortunately it is not on the list for MSFS2024. If I have to, I will buy it again for MSFS204, just make sure it is compatible. It would be great if it was included in MSFS2024. I tested the latest release, unfortunately it does not work. If it should work, please tell me exactly where to copy the files of the latest version sent. Best regards.
hi. we have plans to upgrade this aircraft for FS24 support, but can’t say when it may happen – currently we are busy with other project.
Hi
Im looking to find the controllable and landable cargo truck ; how did i can use it in the sim with tha KA-10 (i have SU12) . thanks . jean
Hi! it’s not finished yet but will be available with next update
I have version 2.7 for the series x. Why are the planes spawning in the air? Thanks
Please clarify your question, maybe you are asking why you spawn in the air instead of flight deck of aircraft carrier?
My aircraft carrier does not have a working catapult, it uses to work for the first few months and now it stopped. The ground crew stands there and stares at me.
First, ensure you have activate “CATAPULT” button on the Aircraft tab of the toolbar. After that, catapult and arrestors script will be activated (that was added to avoid conflict with similar carrier add-ons).
If it still does not work, tell me which platform are you using (PC or Xbox), and how add-on was installed – manually, ingame marketplace etc.
Can you tell me where the scenery in the screenshots is located?
On the worldmap screen, type KUZ or TOPGUN in the search field – you will get all available carriers locations.
Then where do I find the world
map screen?
this one, search field in the left top corner
https://cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/21765140/Screenshot_2020_08_17_13.59.26.png
Well, what other scenery locations are shown in the photos?
To Alex,
It seems that your KA-10M may have a conflict with A2A Simulations
Accu-Sim Comanche 250 for MSFS. When both are installed, the Comanche spawns on the ground surrounded by aircraft carrier flight deck crew, for some reason. It has been reported by a number of people that when your KA-10M is removed from the Community folder the issue disappears.
Here is the link to the A2A Simulations forum: https://a2asimulations.com/forum/posting.php?mode=reply&f=151&t=74847
Thank you! I will investigate this problem.
Also confirming this issue, same thing happens to me
Should be fixed in v2.7.1, please confirm
Hi There,
With the latest version 2.5.1. the teleport functionality is not working for me. In the UI the option “on the deck” and “arrive” are both orange coloured. I tried all combination with real time and real weather but no luck. Can you explain how to get the teleport function working as it did in the previous version >?
As of 12-19-2022 – Microsoft in-game MSFS store version is still v1.41, according to the ‘manifest.json file. Yet the SimMarket version is v2.3.0. Currently, that means this is the fifth patch/update since v1.41 that is hosted on the MSFS store).
According to your post, Microsoft received an update on Monday 05-12-22 for approval. It has been 10 working days now, yet no update on the MSFS copy of the KA10-M.
Is there an issue with purchases made on the MSFS store?
It has status “Testing”, they have not contacted us about issues yet. I can guess many other devs releasing products and updates on holidays which makes MS stuff busy.
MSFS store always will have such problems:
1. updates release delay of 1-4 weeks
2. no branded or mature content
3. no way to mod aircraft files
But same time it has widest audience and easiest installation process. We can only follow their rules and can’t avoid such issues I am afraid.
Hi There,
I tried the ship elevators but with aircraft on the elevator going down or up, the aircraft is rather jumping on the elevator. I assume this is a limitation of FS2020 at the moment ?
Another question, is there a teleport option to teleport the aircraft to the deck or the elevator ?
Thanks Marc.
Hello.
Yes, moving collision surfaces are not calculated by sim quite accurate. It became less noticeable if moving is really slow, but still happens. I have noticed it feels little better when parking brakes engaged, if you are using some other aircraft than Ka-10. Also ensure aircraft parts (like wings or tail) does not touch carrier body.
On moving carrier – currently no way. For static carrier runway and helipad points will be also added in next update. However, you made me think about possible solution as teleport button for the panel – you still should start flight in the air but then get on the deck in one click. We’ll see how it may work.
Hi There,
I see that you added a new test version v2.2.1 on your site.
I purchased mine from simmarket which still is on v2.1.1.
I there a chance I can download this new test version a well ?
Thanks, Marc.
New version available on SimMarket now. Marketplace staff do check each update content manually so it takes about 6-12 hours until update reach customers, depends on time of the day and day of the week.
Hi,
Thanks for the latest version. Teleport feature works for me.
I am puzzled about the real time sync feature.
Can you explain me what it is for ?
Thanks,
Marc.
Let’s review two cases:
1. Live weather AND Real Time are active (in MSFS weather settings)
Each half hour carrier group position will reset to the origin. If you just start the flight, script will teleport carrier group into proper position for this stage of the cycle. This way teleport on deck feature will work as script can predict where carrier is right now, but also all other players flying around (with live weather, real time and real time sync enabled) will see it in almost same position (some inaccuracy may be). So while you landed on moving carrier, other players will see it correctly.
2. Live weather or real time is disabled
Each half hour carrier position will reset as well, so teleport feature will work same way. But because your sim time is random – you will see carrier in wrong position compare to other players. So this solution works for teleport but not for multiplayer experience.
As of 12-02-2022 – Microsoft in-game MSFS store version is still v1.41, according to the ‘manifest.json file. Yet the SimMarket version is v2.11. There is also no evidence of the ‘carrier’ in the MSFS store version.
Is this intentional and if so then why?
If not intentional, when can we expect the MSFS store version to be updated?
All true – MS marketplace current version is 1.x which does not have carrier yet.
We are fixing last issues and will send update for approval on Monday, It will take 5-10 days for MS team to test it and add into marketplace.
As the mechanic for the Kamow Ka 26 at INTERFLUG, I’m looking forward to the Ka-10 for the MSFS and can’t wait!
Hello,
On your KA-10M specification (https://msfs.touching.cloud/mods/ka-10m-hat/) you wrote service ceiling is 2000 meters or 3300 feet. This is incorrect, 2000 meters is 6600 feet. Or perhaps you wanted to write 1000 meters which is indeed 3300 feet. Kindly correct this. Thank you!
Yep, imperial value is incorrect. Thanks for the heads up.